Friday, October 24, 2008
How Long Wait To Get Relaxer After Weave
Hi! I hope you write me something on my blog but now is a bit under construction. A kiss
Thursday, March 20, 2008
Schwarzkopf In Chennai Where Can We Buy

Veamos el siguiente ejemplo:
4 + 3 x 5 – 6 : 2 =
En este ejemplo, los términos son:
4
3 x 5
6 : 2
Si resolvemos cada término la operación sería:
4 + 15 – 3 = 16
Si bien este es un caso muy simple puedo ASOCIAR para obtener el resultado.
Recordemos que la propiedad ASOCIATIVA decía: “A la suma de los positivos le resto la suma de los negativos”. Aplicando esta propiedad, la operación would be:
(4 + 15) - 3 =
19-3 = 16 Let
an example a little more complicated:
-8 + 6 x 4 - 18: 2 + 20: 2 - 5 =
We have the following terms:
-8 6 x 4
18: 2
20: 2 5
The operation would be:
-8 + 24-9 + 10 - 5 =
associate:
( 24 + 10) - (8 + 9 + 5) =
1934 to 1922 = 12
Let's do another example.
8 + 6 x -5 to 4 x -3 =
separate terms
8 6 x 4 x -3 -5
would have
8 + - 30 - - 12 =
In this case we see that we "seal" the sign of the operation with the sign of numbers, to separate using parentheses. This would create
:
8 + (- 30) - (- 12) =
To solve the above operation we have to DELETE BRACKET . To remove parentheses have to look at the sign above the parentheses to remove, if a positive sign (+) signs are in parentheses NO CHANGE , if the sign above the parentheses is negative (-) signs are in parentheses CHANGE, let our case:
8 + (- 30) - (- 12) =
As (- 30) is preceded by an ampersand ( +) is like - 30, ie,
8 to 30 - (- 12) =
Now let the (- 12) and is preceded by a minus sign (-) 12 + 12 becomes, then we would
8 to 30 +12 =
Asocio:
(8 + 12) - 30 =
20-30 = -10
Now let's do an exercise in removing brackets a little longer, let us that the way we're going to accomplish is not the only but, although it is longer and more tedious than others, is how to perform this operation with less risk of error.
Another thing to consider is that, generally, when we have more than one pair of brackets and to tell them apart, are placed in square brackets and, if necessary, keys, we are only going to put parentheses only a matter graph. We
exercise.
6 + 8 - (- 6 + 8 + 6 - (- 8 + 6 + 8 - (- 6 + 8) - 6) + 8) =
first remove the parentheses smaller, I look at the sign The foregoing, as is (-) signs interior change, then:
6 + 8 - (- 6 + 8 + 6 - (- 8 + 6 + 8 + 6 - 8 - 6) + 8) =
We suppressing again the sign that precedes the parentheses to remove it (- ):
6 + 8 - (- 6 + 8 + 6 + 8 - 6 - 8 - 6 + 8 + 6 + 8) =
Last suppression, again sign (-):
6 + 8 + 6 - 8 - 6 - 8 + 6 + 8 + 6 - 8 - 6 to 8 =
As we see, we were left with a succession of additions and subtractions, in the next step we apply Cancel property is, we will seek numbers with the same absolute value but with different signs and "cancel" of the operation, this can be done because the addition or subtraction of these would result in zero, that is, not change the outcome, we will go step by step and I will paint red numbers I'll go canceling, see:
6 + 8 + 6 - 8 - 6 - 8 + 6 + 8 + 6 - 8 - 6 to 8 =
would:
8 + 6 - 8 - 8 + 6 + 8 + 6 - 8 - 6 to 8 =
would:
6 - 8 + 6 + 8 + 6 - 8 - 6 - 8 =
would:
- 8 + 6 + 8 + 6 - 8 - 8 =
would be:
6 + 6 - 8 - 8 =
Finally PARTNERS:
(6 + 6) - (8 + 8) =
12 to 16 = - 4
This way of solving the exercises is longer and perhaps more tedious but, as we said before, is how the least possibility of error we have, well, now let's solve some exercises to take their resolution resolving as DELIVERY in the above manner.
a) - 7 + 5 x -6 to 7 x 4 =
b) 9 - 28: - 2 + 4 x - 3 =
c) 5 + 3 - (- 4 to 5 + 6 + 3 - 4) + 10 =
d) 3 - 4 – ( - 3 – 4 + 3 – ( - 4 + 3 + 4) – 3 ) =
e) 7 – ( - 6 – 4 x -6 – 5 – 6) =
Monday, November 19, 2007
Muvies En Espana En Espanol Gratis
tissues are characterized because their cells are surrounded by an intercellular matrix solid and relatively rigid .
cartilage.
the extracellular which the chondrocytes (cartilage cells) are located in spaces called lacunae.
Functions:
- it supports or support.
- Of the articular surfaces.
- is part of the airways.
Structure:
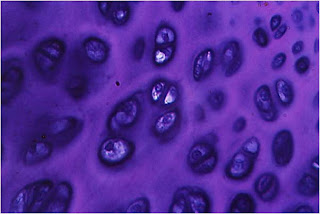
-chondroblasts.
-Chondrocytes.
- • Collagen.• Elastin.• hyaluronic acid• Glycoproteins• Proteoglycans
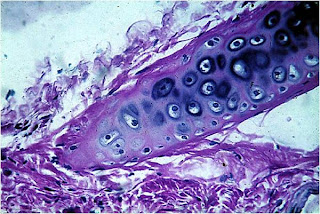
matrix. blood vessels do not penetrate the cartilage matrix
. They feed material broadcasting from the tissue capillaries adjacent .
Types:
According with the abundance and type of fiber in the matrix:
- is the most common.
- has a moderate amount of collagen fibers .
- forms the fetal skeleton, epiphyseal plates , joints, c. sack and large airways.



bone tissue.
Structure:
Trained by:- • Osteoblasts: responsible to produce and secrete the organic part of bone matrix during its formation. Located at the periphery of the tissue.
- • osteocytes are responsible for the maintenance of bone matrix. They are located in cavities or gaps.
- • Osteoclasts, cells responsible for resorption of bone tissue located in Howship gaps.
bone Rating:
is found in flat bones and ends of long bones .

is located in the outer layer of flat bones and bodies of long bones.


functions of bone tissue:
Use Motorcycle Engine In Go Kart
The nervous tissue is scattered by the body interrelate and forming a communication network is the nervous system.
is composed of neurons that are specialized cells in the electrochemical conduction of nerve impulses.
Features:
- It originates from the ectoderm.
-
Its main components are cells surrounded by scarce intercellular material.
-
is located at the Central Nervous System and Peripheral Nervous System .
Structure:
is formed by:- Cells
-
neurons or nerve cells.
-
Neuroglia or supporting cells.

nerve cells or neurons.
are the functional cells of nervous tissue. Are interconnected to form networks.
Functions:
Structure:
- The cell body includes the cytoplasm and nucleus.
- The dendrites. The function of dendrites is to receive stimuli from the environment, epitelialessensoriales cells or other neurons.
- The
axon or axis cylinder. The axon is the transmitter with respect
the nerve impulse, or transmitting the nerve impulse. This has the following structures.
- • myelin sheath.
- • cells Shwann .
- • Ranvier nodules.


Synapse: The
synapses (the gr. σύναψις, "link") are specialized junctions through which cells nervous system send signals to each other and non-neuronal cells such as muscle or glandular .
A synapse between a motor neuron and muscle cell called neuromuscular junction.
synapses allow neurons the central nervous system form a network of neural circuits.
In a prototypical synapse, such as those found in dendritic buttons , Cytoplasmic projections with mushroom from each cell, and in which both ends are crushed against each other. In this area, cell membranes of both cells were close together in a union that allows signaling molecules called neurotransmitters quickly switch to another cell by diffusion . The canal linking the postsynaptic neuron, is about 20 nm wide, and is known as synaptic cleft.

synapses are made between the axon of one neuron and the dendrites or the body of other neurons.
Classification of neurons:
According to the number of extensions.
- Unipolar or seudomonopolares .

According to its function.
- motor neuron. Carry
nerve impulse to the organs peripheral terminals.
- sensory neuron.receive momentum generated by stimulation and transported to the central nervous system.
- intermediate neuron.interconnect two neurons: a motor with a sensitive, sensitive to sensory, motor to another.
supporting cells.
surround the neurons and play support functions, defense, nutrition and adjusting the composition of intercellular material.


Nerve Fibers.
myelin formed by oligodendrocytes ( Melina).
nerve fibers are composed by grouping a large number of axons and these in turn are combined to form the nerves.
Nervios.
- Las aferentes llevan a los centros las informaciones procedentes del organismo y del medio ambiente.
- Las fibras eferentes transmiten impulsos de los centros nerviosos a los órganos efectores controlled by these centers.
- nerves may be sensory, motor and mostly mixed.
functions of nervous tissue:
- from collects information from sensory receptors .
-
process this information, providing memory system.
-
generates proper signals to
Effector cells


















