tissue is called to the group of cells with a specific structure to perform a specialized function, vital for the body.
Group of cells, fibers and cell products forming a set number of structural and fulfilling the same function.
Rating:
According to its nature and function
differ in:
1 .- epithelial tissue.
- epithelial tissue lining.
- glandular epithelial tissue.
- sensory epithelial tissue.
2 .- Connective tissue.
- connective tissue itself.
- specialized connective tissue:
- bone tissue.
- cartilage.
- blood tissue.
3 .- muscle tissue.
- striated muscle.
- smooth muscle.
- heart muscle.
Epithelial Tissue:
The epithelium is the tissue formed by one or more layers of cells juxtaposed to form the inner lining of the cavities, hollow organs, ducts of the body and skin, and also are the mucous membranes and glands.
is that generally consists of polyhedral cells, juxtaposed, among which there is little intercellular substance.
Features:
consists of cells closely set together. With little or no intercellular substance. The cells are arranged in a single layer or multiple layers.
Structure:
- Cells:
- flat cells
- cubic cells
- cylindrical cells.

Union means:
- - Union Cement
- - desmosomes
- - Bands closing
- - Unions close
- - interdigitating membranes
- - membrane folds
- - Membrane basal
Polarity:
Each cell has three types of surfaces apical surface (free) a number variable side surfaces adjacent to neighboring cells and a basal surface attached to the basal layer.

embryonic epithelial tissue Source:
, originating from the three layers germ. Ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm.
Ectoderm:
- surface of the skin epithelium.
- sensory epithelium (nasal mucosa, retina, inner ear, taste buds).
Mesoderm:
are derived from this:
- epithelium of the seminiferous tubules in the testes and ovaries germinal epithelium.
- Endothelium of the heart and blood vessels.
- pericardium (membrane that surrounds the heart), pleura (membrane covering the lungs and inside the chest) and peritoneum (lining of the abdominal organs and inside the abdomen).
- brain membranes (meninges), inner ear, eye and genital tract.
Endoderm:
- Epithelium of the digestive tract and accessory glands (liver, pancreas).
- epithelium of the airways and lungs.
Depending on the function of the epithelium:
- - lining epithelium or squamous
- - lar glandular epithelium.

 Skin Glands
Skin Glands Depending on the shape of epithelial cells:
- - squamous epithelium or squamous. Squamous cells are flat and similar to plates.
- - cuboidal epithelium. cuboid cells are polygonal with
height and width similar.
- - Epithelium prismatic or cylindrical. cylindrical cells are polygonal with greater height than width.



Depending on the number of layers of cells that form:
- - simple epithelium. A single layer.
- - stratified epithelium. Two or more cell layers.
• All the cells rest on the sheet baseline.


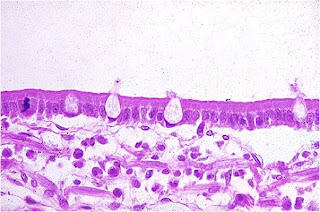
cilíndricas.
cubiertas de cilios o microvellosidades .
propulsion of mucus.



Epitelio cilíndrico seudoestratificado.


some large glands.
lining.

glandular epithelial tissue:
Glands:
are single cells or groups of cells specialized for secretion. All glands arise in early development, from the lining or covering epithelium.
glandular epithelial tissue:
is characterized by the property they own their cells produce substances that pass then to the outside or the circulation, to be distributed throughout the body.
- unicellular glands. • Sometimes, among the cells lining epithelium isolated glandular cells interspersed.

- • multicellular gland. entire lining epithelium is at once secretory

Glands:
can be of two types according to where
Pourtheir secretions


| Category | GLANDS EXOCRINE | GLANDS ENDOCRINE |
| Liberation secretions | Through ducts | A circulation |
| Number cells | Unicelares or multicellular | multicellular |
| secretory products | Protein glycoproteins and some lipids | peptide hormones and hormones. steroid |
function of epithelia:
- Injury Protection. Covering (epidermis)
- discharge of substances (glands)
- substance absorption (intestine, kidney)
- sensory reception (sense organ)
- sensory function. Excretion
- (Kidney)
- Transportation (lung)
- digestion (digestive tract)














0 comments:
Post a Comment