tissues are characterized because their cells are surrounded by an intercellular matrix solid and relatively rigid .
cartilage.
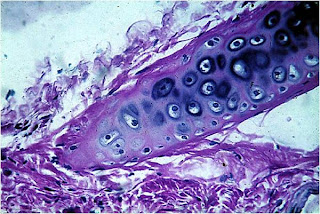
has rigid consistency. Its surface is slightly elastic and very smooth.
is composed of a rich array
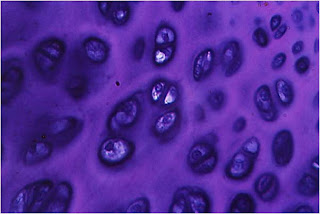
the extracellular which the chondrocytes (cartilage cells) are located in spaces called lacunae.
Functions:
- it supports or support.
- Of the articular surfaces.
- is part of the airways.
Structure:
• cells.
-chondroblasts.
-Chondrocytes.
-chondroblasts.
-Chondrocytes.
• Matrix extracellular. It consists of:
Types:
- • Collagen.• Elastin.• hyaluronic acid• Glycoproteins• Proteoglycans

Chondrocytes synthesize and secrete organic components of the extracellular matrix. The death of the cells leads to degeneration
matrix. blood vessels do not penetrate the cartilage matrix
. They feed material broadcasting from the tissue capillaries adjacent .
is surrounded by the perichondrium corresponding to dense connective tissue.
Types:
According with the abundance and type of fiber in the matrix:
• hyaline cartilage:
- is the most common.
- has a moderate amount of collagen fibers .
- forms the fetal skeleton, epiphyseal plates , joints, c. sack and large airways.


• Elastic cartilage:
• structure similar to hyaline cartilage.
• has collagen fibers and abundant elastin fibers.
• is located in the outer ear, trunk Eustáquio , epiglottis, cartilage corniculate and cuneiform of the larynx.
• Fibrous Cartilage:
• The matrix consists almost entirely fibers collagen forming a network.
• Found in intervertebral discs, symphysis pubis.






bone tissue.
Bone tissue is a type of connective tissue is characterized by its rigidity and its resistance both tensile and compressive .
Structure:
Trained by: • Bone matrix: intercellular calcified material.
• Cells:
- • Osteoblasts: responsible to produce and secrete the organic part of bone matrix during its formation. Located at the periphery of the tissue.
- • osteocytes are responsible for the maintenance of bone matrix. They are located in cavities or gaps.
- • Osteoclasts, cells responsible for resorption of bone tissue located in Howship gaps.
• The bone matrix is \u200b\u200bdeposited inorganic salts granted hardness. These are:
• calcium phosphate.
• calcium carbonate.
• Calcium fluoride.
• magnesium fluoride.
bone Rating:
• spongy bone:
Formed by thin trabeculae. Presents bone marrow-filled cavities.
• Function: involved in hematopoiesis (blood formation).
is found in flat bones and ends of long bones .



is found in flat bones and ends of long bones .

• Compact bone:
Formed by plates or concentric rings around central channel called Havers channels. channels Havers are connected to other channels channels called Volkmann. Among the concentric lamellae of mineralized matrix there are small holes or gaps where are the osteocytes.
is located in the outer layer of flat bones and bodies of long bones.


functions of bone tissue:
• Form the skeleton that supports the body.
• constitute the insertion point of muscles .
• Contains the bone marrow where blood cells are formed.








0 comments:
Post a Comment